Pythagoras theorem
In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides.
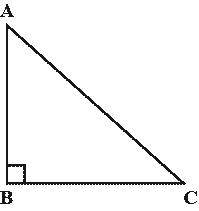
\(AC^2=AB^2+BC^2\)
Proof
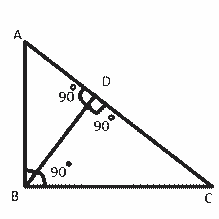
We know, △ADB ~ △ABC
Therefore, \(\tfrac{AD}{AB}=\tfrac{AB}{AC} \)(corresponding sides of similar triangles)
Or, AB2 = AD × AC ……………………………..……..(1)
Also, △BDC ~△ABC
Therefore, \(\tfrac{CD}{BC}=\tfrac{BC}{AC}\) (corresponding sides of similar triangles)
Or, BC2= CD × AC ……………………………………..(2)
Adding the equations (1) and (2) we get,
AB2 + BC2 = AD × AC + CD × AC
AB2 + BC2 = AC (AD + CD)
Since, AD + CD = AC
Therefore, AC2 = AB2 + BC2
Hence, the Pythagorean theorem is proved.
Download img file for quick revision offline