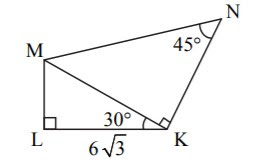
Solution::
In \(\triangle \space LKM\) ,
\(tan30^∘ ={ML\over LK} \)
\(\Rightarrow ML=6\sqrt { 3 } \times \dfrac { 1 }{ \sqrt { 3 } } =6\)
\(\cos { { 30 }^{ \circ } } =\frac { LK }{ MK }\)
\( \Rightarrow MK=\dfrac { LK }{ \cos { { 30 }^{ \circ } } } =\dfrac { 6\sqrt { 3 } }{ \dfrac { \sqrt { 3 } }{ 2 } } =12\)
NK=MK (Side opposite to equal angles )
\(\therefore NK = 12\)
In\(\triangle MKN\)
\(\sin 45^{\circ}=\dfrac{NK}{MN}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt2}=\dfrac{12}{MN}\)
\(MN=12\sqrt2\)
Perimeter of ◻MNKL =MN+NK+Lk+ML
\(perimeter \space = 12\sqrt{2}+12+6\sqrt{3}+6\)
\(= 18+6(2\sqrt2+\sqrt3)\) unit {if cm then cm}
Video solution ::