(i) The circuit for this case is shown below.
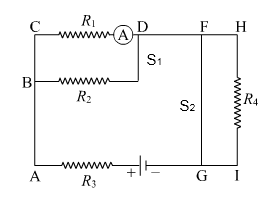
R4 is shunted by S2 . Hence the Resistance of this combination will be practically zero
R1 and R2 in parallel
∴ \(\frac{1}{R_p} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2}\)
∴ \(R_p = \frac{R_1 R_2}{R_1 + R_2}\)
R3 and Rp in series
∴ Rs = R3 + Rp
∴ I3 = \(\frac{V}{R_s}\) = \(\frac{V}{R_3 + R_p}\)
V1= V-I3R3
= V- \(\frac{R_3 V}{R_3 + R_p}\)
= V \((1-\frac{R_3}{R_3 + R_p})\)
= V\((\frac{R_p}{R_3 + R_p})\)
∴ I1= V1/R1 = \(\frac{V}{R_1}(\frac{R_p}{R_3 + R_p})\)
Similarly
I2 = \(\frac{V}{R_2}(\frac{R_p}{R_3 + R_p})\)
-
(ii) Both S1 and S2 are open.
Answer
The circuit for this case is shown below.
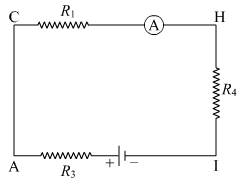
Here, R1, R4 and R3 are in series. Therefore, the equivalent resistance of the circuit is
Req=R1+R3+R4

Hence, the current flowing in the circuit is
I= \(\frac{V}{R_(eq)}\) = \(\frac{V}{R_1+R_3+R_4}\)
where, V is the potential difference of the battery.
-
(iii) S1 is closed but S2 is open.
The circuit for this case is shown below.
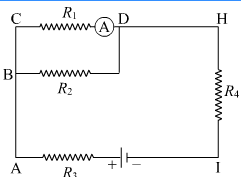
Here, R1 and R2 are in parallel. Their effective resistance is
R'=\(\frac{R_1×R_2}{R_1+R_2}\)
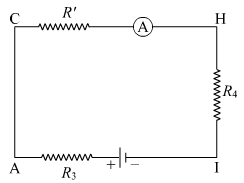
Now, R3, R' and R4 are in series. Thus, the equivalent resistance of the circuit is
Req= \(\frac{R_1×R_2}{R_1+R_2} + R_3 + R_4 \)
= \(\frac{R_1 R_2 +R_3 R_1 + R_3 R_2 + R_4 R_1 +R_4 R_2}{R_1+R_2}\)
Hence, the current flowing in the circuit is
I=V/Req= \(\frac{v}{\frac{R_1 R_2 +R_3 R_1 + R_3 R_2 + R_4 R_1 +R_4 R_2}{R_1+R_2}}\)
= \(\frac{V(R_1+R_2)}{R_1 R_2 +R_3 R_1 + R_3 R_2 + R_4 R_1 +R_4 R_2}\)
where, V is the potential difference of the battery.