A. What is PEAS descriptor? Give PEAS descriptor for robot maid for cleaning the house.
PEAS stands for Performance measure, Environment, Actuators, and Sensors. It is a framework used in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) to describe and analyze intelligent agent systems. Each letter in PEAS corresponds to a different aspect of the system:
- Performance Measure: This defines how the success of the system will be measured. It specifies the criteria or metrics that determine the effectiveness of the intelligent agent in achieving its goals.
- Environment: This describes the external context or surroundings in which the intelligent agent operates. The environment includes everything that is not part of the agent but can be affected by the agent’s actions.
- Actuators: Actuators are the components of the agent that carry out the actions or execute the strategies decided upon by the agent. These actions are intended to affect the environment in some way.
- Sensors: Sensors are the components that allow the agent to perceive or receive information from the environment. They provide the agent with the necessary input to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions.
PEAS descriptor for robot maid for cleaning the house.
| Component |
Description |
| Performance Measure |
Efficiency in cleaning, time taken to complete tasks, cleanliness achieved, ability to adapt to different types of surfaces, and user satisfaction with the cleaning results. |
| Environment |
Indoor household environment, which includes various rooms, furniture, floors, carpets, and potentially obstacles or objects that the robot may encounter during cleaning tasks. |
| Actuators |
Cleaning tools such as brushes, vacuuming mechanism, mopping mechanism, and mobility systems for navigation around the house. |
| Sensors |
Cameras, infrared sensors, and pressure sensors for navigation, object detection, and avoidance. Dirt sensors to detect dirty areas. |
B. Discuss different applications of AI.
Here are 10 major applications of artificial intelligence:
- Virtual Assistants – Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant etc. that understand voices and languages to answer questions and perform tasks.
- Recommendation Systems – Netflix, Amazon etc. use AI to study customer behavior and recommend products and content.
- Computer Vision – Facial recognition, image classification, object detection for surveillance, self-driving cars, photo organizing.
- Natural Language Processing – Chatbots, sentiment analysis, text summarization, language translation, conversational AI.
- Predictive Analytics – Detect patterns in data to make predictions about future events and outcomes in areas like predictive maintenance, healthcare, etc.
- Autonomous Vehicles – AI allows self-driving cars to perceive environment, detect objects, signs, pedestrians and navigate without human intervention.
- Robotics – AI makes industrial and service robots smarter, more perceptive, versatile and collaborative to improve business efficiency.
- Fraud Prevention – Real-time fraud detection in credit cards, healthcare, insurance by analyzing data patterns and user behavior.
- Medical Diagnosis – AI assists doctors in diagnosing diseases, treatment planning through synthesis of patient records and medical data.
- Personalization – AI analyzes customer history and behavior to provide tailored recommendations and personalization across shopping, content platforms, marketing campaigns etc.
C. Draw and explain architecture of Expert System.
An expert system is a computer program that is designed to solve complex problems and to provide decision-making ability like a human expert. It performs this by extracting knowledge from its knowledge base using the reasoning and inference rules according to the user queries.
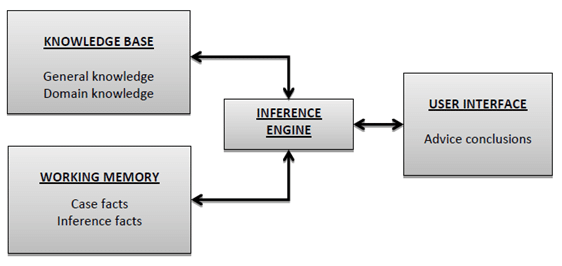
- User Interface (UI):
- This is the front end of the expert system that interacts with the user.
- It provides a way for users to input information and receive output from the system.
- The UI can take various forms, such as a graphical user interface (GUI) or a command-line interface (CLI), depending on the application.
- Knowledge Base (KB):
- The knowledge base is a central component of the expert system that stores information about the domain.
- It includes two main components: facts and rules.
- Facts: These are pieces of information about the specific case or domain. Facts are typically represented in the form of statements.
- Rules: These are logical statements that define relationships between various facts. Rules are used by the inference engine to make decisions.
- Inference Engine:
- The inference engine is responsible for drawing conclusions based on the information stored in the knowledge base.
- It uses various reasoning strategies, such as forward chaining (data-driven) or backward chaining (goal-driven), to infer new facts or make decisions.
- The inference engine interprets the rules and applies them to the given set of facts to derive new conclusions.
- Working Memory:
- Working memory is a temporary storage area where the current set of facts and conclusions are kept during the inference process.
- It is used by the inference engine to manipulate and update information as it processes the rules.
https://www.doubtly.in/blog/artificial-intelligence-question-paper-solutions-ai-ds-ai-ml-cseds-aiml/
https://www.doubtly.in/blog/artificial-intelligence-question-paper-solutions-ai-ds-ai-ml-cseds-aiml/
https://www.doubtly.in/blog/artificial-intelligence-question-paper-solutions-ai-ds-ai-ml-cseds-aiml/