The agents which are developed having their end uses as building blocks are called utility-based agents. When there are multiple possible alternatives, then to decide which one is best, utility-based agents are used. They choose actions based on a preference (utility) for each state. Sometimes achieving the desired goal is not enough. We may look for a quicker, safer, cheaper trip to reach a destination. Agent happiness should be taken into consideration. Utility describes how “happy” the agent is. Because of the uncertainty in the world, a utility agent chooses the action that maximizes the expected utility. A utility function maps a state onto a real number which describes the associated degree of happiness.
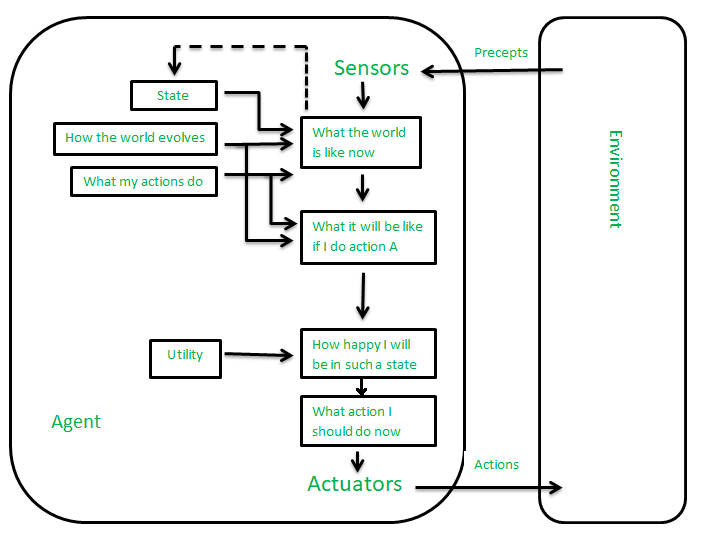
Differnces
Utility-Based Agent:
- Decisions based on maximizing expected utility.
- Uses a utility function to represent preferences.
- No explicit model of the environment.
- Flexibility in adapting to different environments.
- Decision-making without detailed understanding of the world.
Model-Based Agent:
- Decisions rely on simulating the environment through an internal model.
- Maintains an explicit internal model of the environment.
- Requires modifications to the model for adaptation.
- Provides a detailed understanding of the environment.
- Decision-making involves explicit reasoning about the world state.