The Cisco Service-Oriented Network Architecture (SONA) is a conceptual architecture that describes how to design networks to be more agile, efficient, and scalable.
SONA is based on the principles of service orientation, which means that the network is designed to provide services to applications rather than just providing connectivity. This means that the network is more flexible and can be more easily adapted to changing business needs.
SONA consists of three layers:
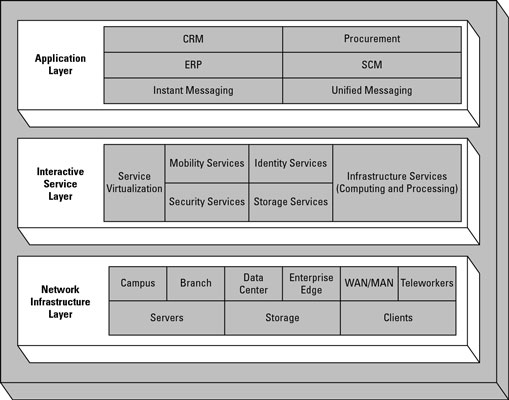
- The Network Infrastructure Layer: The Network Infrastructure Layer is the foundation of the SONA architecture. It provides the physical and virtual resources that are used to deliver network services. This layer is made up of the following components:
- Network devices: Network devices such as routers, switches, and firewalls are responsible for routing traffic, providing security, and other network functions.
- Servers: Servers are responsible for running applications and providing storage.
- Clients: Clients are the devices that users use to access the network, such as computers, laptops, and smartphones.
- The Interactive Services Layer: The Interactive Services Layer provides the network services that are used by applications. This layer is made up of the following components:
- Application services: Application services are the network services that are used by applications to perform specific tasks, such as security, mobility, and storage.
- Business services: Business services are the network services that are used by business processes to support their operations, such as customer relationship management (CRM) and supply chain management (SCM).
- Collaboration services: Collaboration services are the network services that are used by users to collaborate with each other, such as video conferencing and instant messaging.
- The Applications Layer: The Applications Layer is the top layer of the SONA architecture. It contains the applications that are used by users. Applications can be anything from web applications to mobile apps to desktop applications.