[…] functions of protocols of ssl : https://www.doubtly.in/q/enlist-functions-protocols-ssl/ […]
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) provides security to the data that is transferred between web browser and server. SSL encrypts the link between a web server and a browser which ensures that all data passed between them remain private and free from attack.
Secure Socket Layer Protocols:
- SSL record protocol
- Handshake protocol
- Change-cipher spec protocol
- Alert protocol
- SSL Record Protocol: The SSL record protocol is responsible for encapsulating higher-level protocol data (such as HTTP) for transmission over the network. It also provides confidentiality, integrity, and authentication services through encryption and message authentication codes (MACs).
In the SSL Record Protocol application data is divided into fragments. The fragment is compressed and then encrypted MAC (Message Authentication Code) generated by algorithms like SHA (Secure Hash Protocol) and MD5 (Message Digest) is appended. After that encryption of the data is done and in last SSL header is appended to the data.
- Handshake Protocol: The SSL handshake protocol is used to establish a secure connection between the client and the server. During the handshake, the client and server negotiate cryptographic parameters, authenticate each other’s identities using digital certificates, and exchange cryptographic keys for encryption and message authentication. The handshake protocol ensures the confidentiality and integrity of the exchanged data.
Handshake protocol uses four phases to complete its cycle.
- Phase-1: In Phase-1 both Client and Server send hello-packets to each other. In this IP session, cipher suite and protocol version are exchanged for security purposes.
- Phase-2: Server sends his certificate and Server-key-exchange. The server end phase-2 by sending the Server-hello-end packet.
- Phase-3: In this phase, Client replies to the server by sending his certificate and Client-exchange-key.
- Phase-4: In Phase-4 Change-cipher suite occurs and after this the Handshake Protocol ends.
- Change Cipher Spec Protocol: The change cipher spec protocol is a simple protocol used to signal transitions in the SSL/TLS connection state. It consists of a single message, the “change cipher spec” message, which indicates that subsequent data sent by the sender will be protected using the negotiated cryptographic parameters. This protocol is essential for synchronizing encryption settings between the client and server.
Change-cipher protocol consists of a single message which is 1 byte in length and can have only one value. This protocol’s purpose is to cause the pending state to be copied into the current state.

- Alert Protocol: The alert protocol is used to convey SSL-related alert messages between the client and server. These alert messages can indicate various conditions, including errors, warnings, or other status information. Alerts can be used to handle exceptional conditions during the SSL handshake or data transmission, such as certificate validation failures or protocol version mismatches.
This protocol is used to convey SSL-related alerts to the peer entity. Each message in this protocol contains 2 bytes.
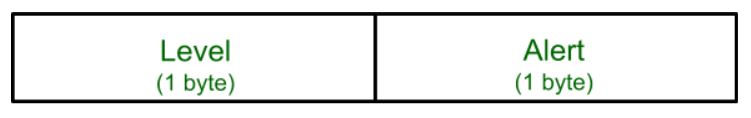
The level is further classified into two parts:
Warning (level = 1):
This Alert has no impact on the connection between sender and receiver. Some of them are:Bad certificate: When the received certificate is corrupt.
No certificate: When an appropriate certificate is not available.
Certificate expired: When a certificate has expired.
Certificate unknown: When some other unspecified issue arose in processing the certificate, rendering it unacceptable.
Close notify: It notifies that the sender will no longer send any messages in the connection.Unsupported certificate: The type of certificate received is not supported.
Certificate revoked: The certificate received is in revocation list.
Fatal Error (level = 2):
This Alert breaks the connection between sender and receiver. The connection will be stopped, cannot be resumed but can be restarted. Some of them are :
Handshake failure: When the sender is unable to negotiate an acceptable set of security parameters given the options available.
Decompression failure: When the decompression function receives improper input.
Illegal parameters: When a field is out of range or inconsistent with other fields.
Bad record MAC: When an incorrect MAC was received.
Unexpected message: When an inappropriate message is received.
Reference : https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/secure-socket-layer-ssl/



[…] functions of protocols of ssl : https://www.doubtly.in/q/enlist-functions-protocols-ssl/ […]